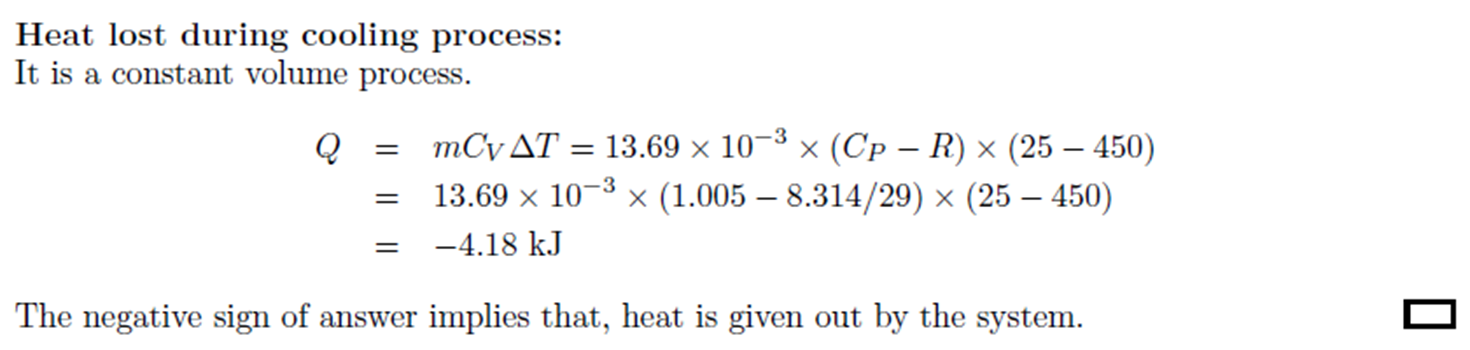Unit-3: First Law of Thermodynamics
Completion requirements
Example: Constant Pressure Heating, Constant Volume Cooling
Example:
Constant Pressure Heating, Constant Volume
Cooling
A 28 liter rigid container is open to the atmosphere, and heat is added to the
bottom of the container until the air temperature inside reaches 450oC. The container is then quickly sealed,
removed from the heating source, and allowed to cool to room temperature of 25oC. How much heat is lost during the
cooling process? (CP
of air = 1.005 kJ.kg-1.oC-1)