14 - Conduction - Critical Radius of Insulation
Completion requirements
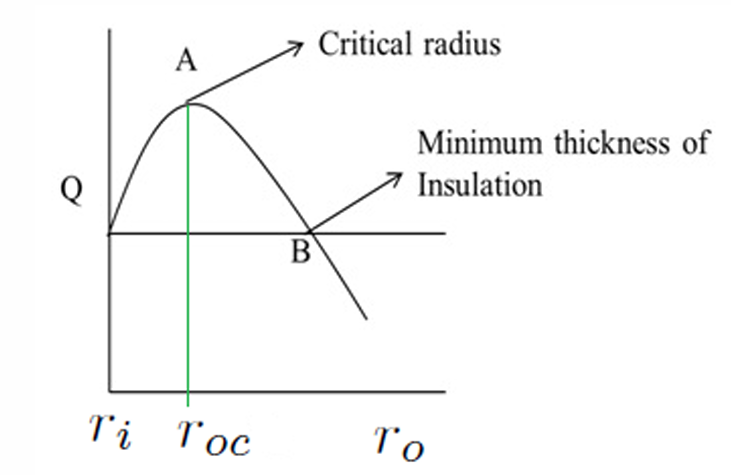
7. Insulation Thickness vs. Heat Loss for Curved Surfaces
\[\begin{aligned}
r_{oc} = \left\{ \begin{array}{cl} \dfrac{k}{h} & \text{for cylinder} \\ \ & \ \\ \dfrac{2k}{h} & \text{for sphere} \end{array} \right. \end{aligned}\] Heat loss from an insulated pipe varies with radius of insulation. Heat loss is maximum at critical radius. The thickness of insulation corresponding to critical radius of insulation is known as critical insulation thickness.
If outside radius of the pipe is smaller than the critical radius of the insulation, one does not have to insulate to save heat loss. But we do not want to leave hot pipes bare for safety reasons.
If the insulating material is chosen in such a way that \(r_{oc}\le r_i\), then any addition of insulation leads to decrease in heat loss.
