16 - Conduction - Heat Generation
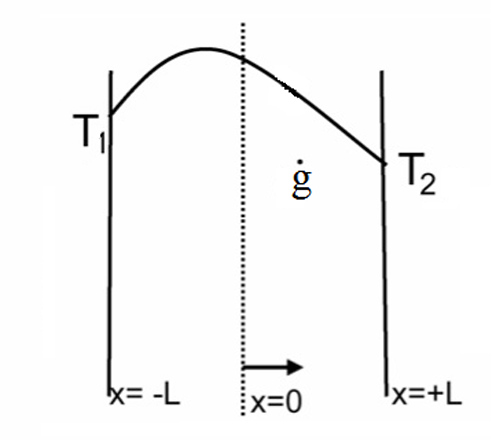
7. Plane Wall with Uniform Heat Generation (surfaces at maintained at different temperatures)
\[\frac{d^2T}{dx^2} = -\frac{\dot{g}}{k}\] Differentiating, we get \[\frac{dT}{dx} = -\frac{\dot{g}x}{k} + C_1\] Differentiating further, we get \[T = -\frac{\dot{g}x^2}{2k} + C_1x + C_2 \tag*{(1)}\]
Boundary conditions: \[\begin{aligned} T&= T_1 \qquad & \text{ at } x&=-L \\ T&=T_2 & \text{ at } x&=L \end{aligned}\]
From B.C. 1 and 2, 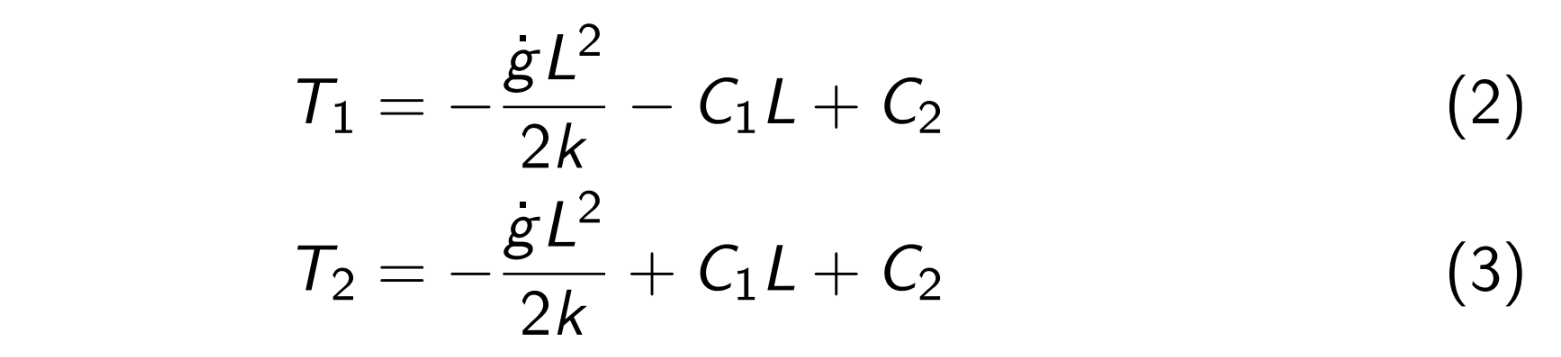
Adding Eqns.(2) and (3), we get 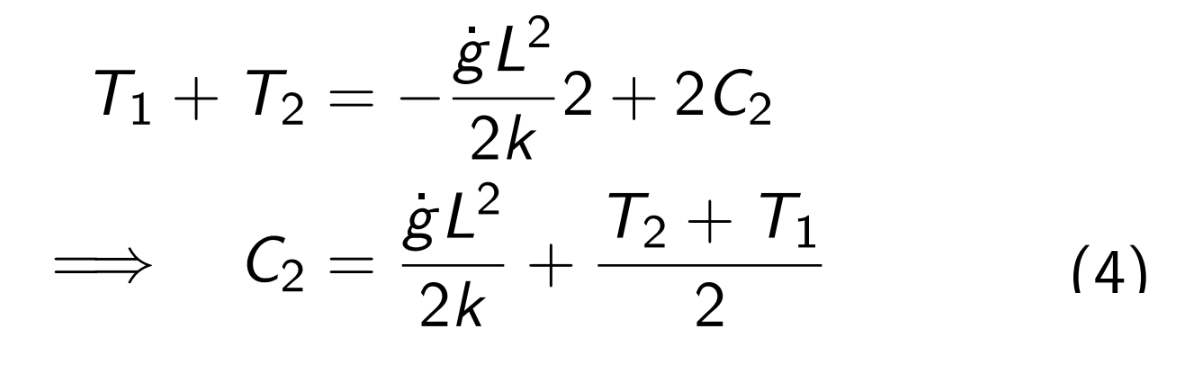
Eqn.(3) \(-\) Eqn.(2) \(\Longrightarrow\) \[C_1 = \frac{T_2-T_1}{2L} \tag*{(5)}\] Using Eqns.(4) and (5) in Eqn.(1), we get \[\begin{aligned} T &= -\frac{\dot{g}x^2}{2k} + \frac{T_2-T_1}{2L}x + \frac{\dot{g}L^2}{2k} + \frac{T_2+T_1}{2} \\ &= \frac{\dot{g}L^2}{2k}-\frac{\dot{g}x^2}{2k} + \frac{T_2-T_1}{2}\frac{x}{L} + \frac{T_2+T_1}{2} \end{aligned}\] i.e., \[\boxed {T = \frac{\dot{g}L^2}{2k}\left(1-\frac{x^2}{L^2} \right) + \frac{T_2-T_1}{2}\frac{x}{L} + \frac{T_2+T_1}{2}}\]
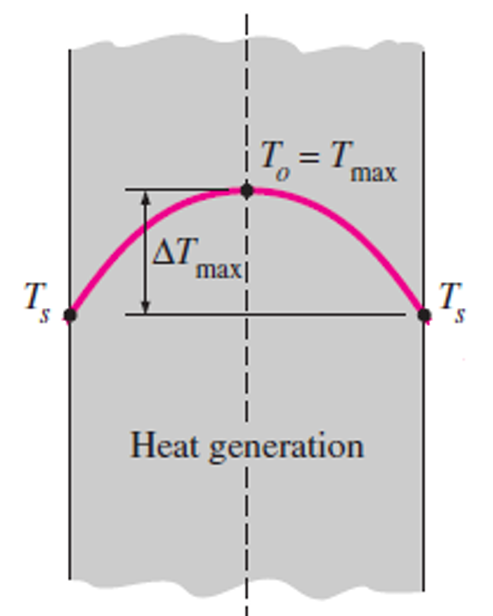
For \(T_1=T_2=T_s\), we get \[\boxed{T = \frac{\dot{g}L^2}{2k}\left(1-\frac{x^2}{L^2} \right) + T_s}\] The maximum temperature exists at the midplane. \[T_{\text{max}} = T(0) = \frac{\dot{g}L^2}{2k} + T_s\]