17-Heat Exchangers - LMTD Method
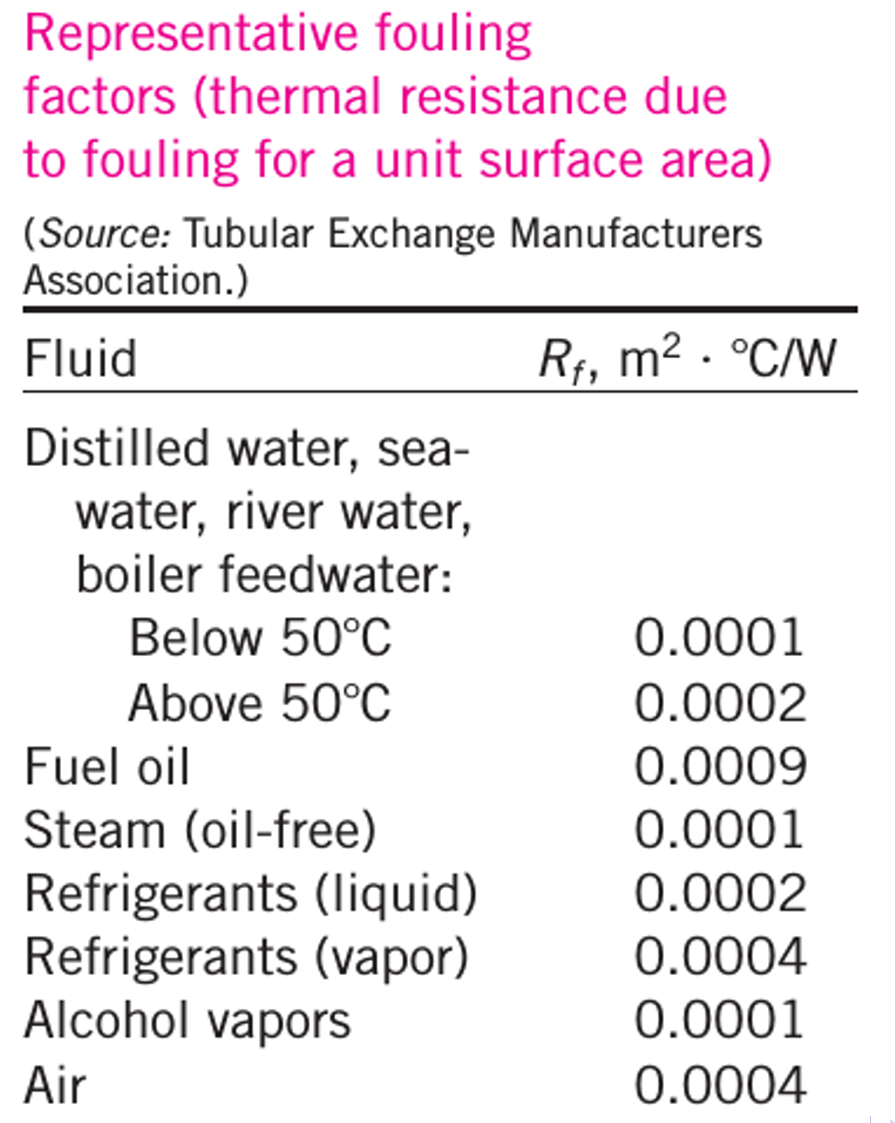
15. Fouling Factor
Over a time period of heat exchanger operation the surface of the heat exchanger may be coated by the various deposits present in the flow system. These deposits are known as scales. These scales provide another resistance and usually decrease the performance of the heat exchangers. The overall effect is usually represented by dirt factor or fouling factor, or fouling resistance, \(R_f\) which must be included for the calculation of overall heat transfer coefficient. \[\boxed{R_f = \frac{1}{U_{\text{dirty}}} - \frac{1}{U_{\text{clean}}} }\] Thus to determine the \(R_f\), it is very important to know \(U_{\text{clean}}\) for the new heat exchanger. The \(U_{\text{clean}}\) data must be kept securely to obtain the \(R_f\), at any time of the exchanger’s life.