Instant Notes
-
The equilibrium between vapor of ideal gas mixture (\(\hat{\phi_i}=1\)) and liquid of ideal solution (\(\gamma_i=1\)) is written as \[y_iP = x_i f_i\] For low pressures, fugacity of component \(i\) in the liquid state (\(f_i\)) can be taken as the vapor pressure (\(P_i^{\text{sat}}\)). Hence, we get \[y_iP = x_iP_i^{\text{sat}} \tag*{(Raoult's law)}\] The above equation is known as Raoult’s law.
VLE of system obeying Raoult’s law is represented in Figs.(27) and (28).
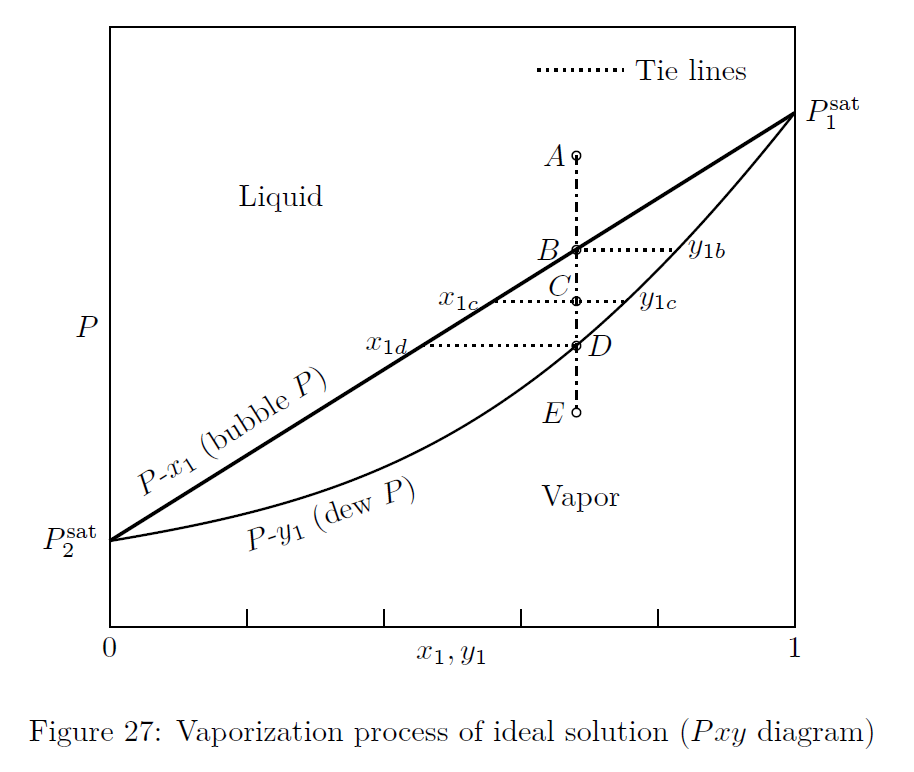
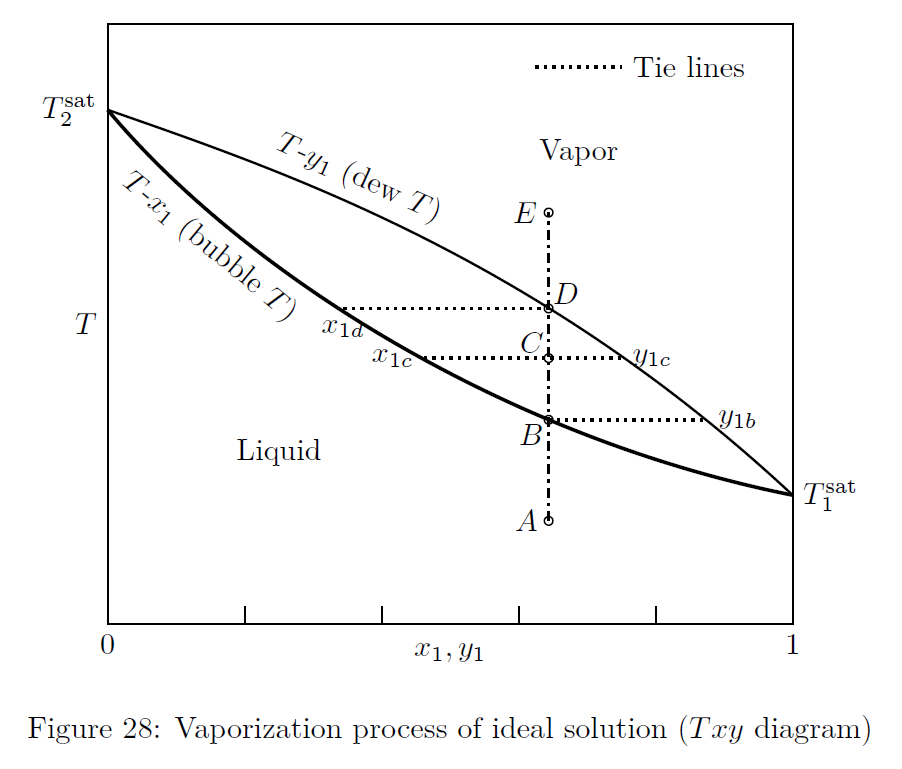
The dew-point pressure, of a system is defined as the pressure at which an infinitesimal quantity of liquid is in equilibrium with a large quantity of vapor.
At the bubble-point, the system is essentially liquid, except for an infinitesimal amount of vapor.
