1. Stoichiometry
Process Streams
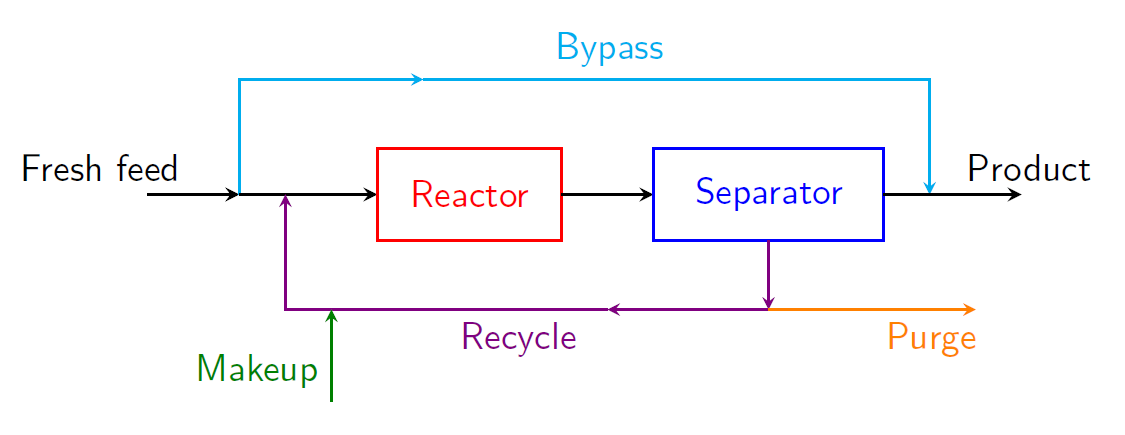
There are various streams entering / leaving a process, namely: feed, product, recycle, bypass, purge, makeup, as shown in previous page.
Recycle is the operation or a process step whereby a part or fraction of the products from the reactor is returned and mixed with the incoming fresh feed to the reactor.
In a reactive process, there is generally some unreacted feed material found in the product mixture. In order to reduce cost and increase the overall conversion, the unreacted material is often separated and reused in a recycle loop. By passing a reactant molecule through the process several times, its chances to react and convert to product are increased.
Other reasons to recycle part of a stream include recovery of valuable materials, such as catalysts, improved temperature control over a process, and decreased waste of working (carrier) fluid.
Bypass Stream—one that skips one or more stages of the process and goes directly to another downstream stage.
Bypass is useful, for example, for decreasing the extent of conversion of input materials or for providing improved control over stream temperatures.
Purge Stream—a stream bled off to remove an accumulation of inerts or unwanted material that might otherwise buildup in the recycle stream.
Purge streams are often encountered together with recycle streams, since recycling makes a process particularly susceptible to accumulation of undesired species. This purge fraction is generally only a few percent of the recycle flow rate.
