2. Humidification
Humidification Terminologies
-
Molal Absolute Humidity:
Moles of vapor per mole of vapor-free gas is called molal absolute humidity (\(H_m\)). \[H_m= \frac{\text{moles of vapor}}{\text{moles of dry air}}=\frac{n_W}{n_A} = \frac{P_W}{P_A} = \frac{P_W}{P-P_W} \quad \frac{\text{mol vapor}}{\text{mol dry air}}\]
-
Absolute Humidity:
The mass of vapor per unit mass of vapor free gas is called absolute humidity (\(H_a\)) \[H_a=\frac{n_W}{n_A}\frac{M_W}{M_A} = \frac{P_W}{P-P_W} \frac{M_W}{M_A} \quad \frac{\text{kg vapor}} {\text{kg dry air}}\]
-
Percentage Humidity:
Percentage humidity is the ratio of actual absolute humidity to the absolute saturation humidity. \[\% H =\frac{H_a}{H_a^{\text{sat}}}\times100\]
-
Dry Bulb Temperature (DBT):
The temperature of a vapor-gas mixture as recorded by immersing the bulb of a thermometer in the mixture is called dry-bulb temperature.
-
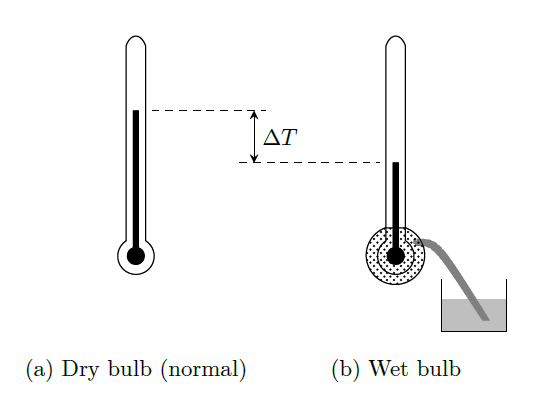
Wet Bulb Temperature (WBT):
Wet bulb temperature is the steady-state temperature of the vapor-gas mixture measured by a thermometer whose bulb is covered with a wet wick or saturated completely by the same fluid.
The bulb of the thermometer is covered by a liquid. This when contacted with the vapor-gas mixture the liquid is evaporated by losing its latent heat of vaporization. This latent heat of vaporization is transferred from the vapor-gas mixture and loses its sensible heat. Hence, the temperature is less when the wet bulb temperature is measured. \[\text{WBT}< \text{DBT} \text{ (except at 100% saturation)}\] The difference between DBT and WBT is called wet bulb depression.
Dew Point (DP):
It is the temperature at which a vapor-gas mixture becomes saturated when cooled at constant pressure in the absence of the liquid.
When the temperature is reduced further less than the DP, the condensation of the saturated vapor occurs.
At dew point, partial pressure of the vapor in the mixture = the vapor pressure of the liquid.
\[\text{At dew point, } \quad \text{DBT} = \text{WBT}\]
