3. Cooling Tower
Cooling of Water in a Cooling Tower
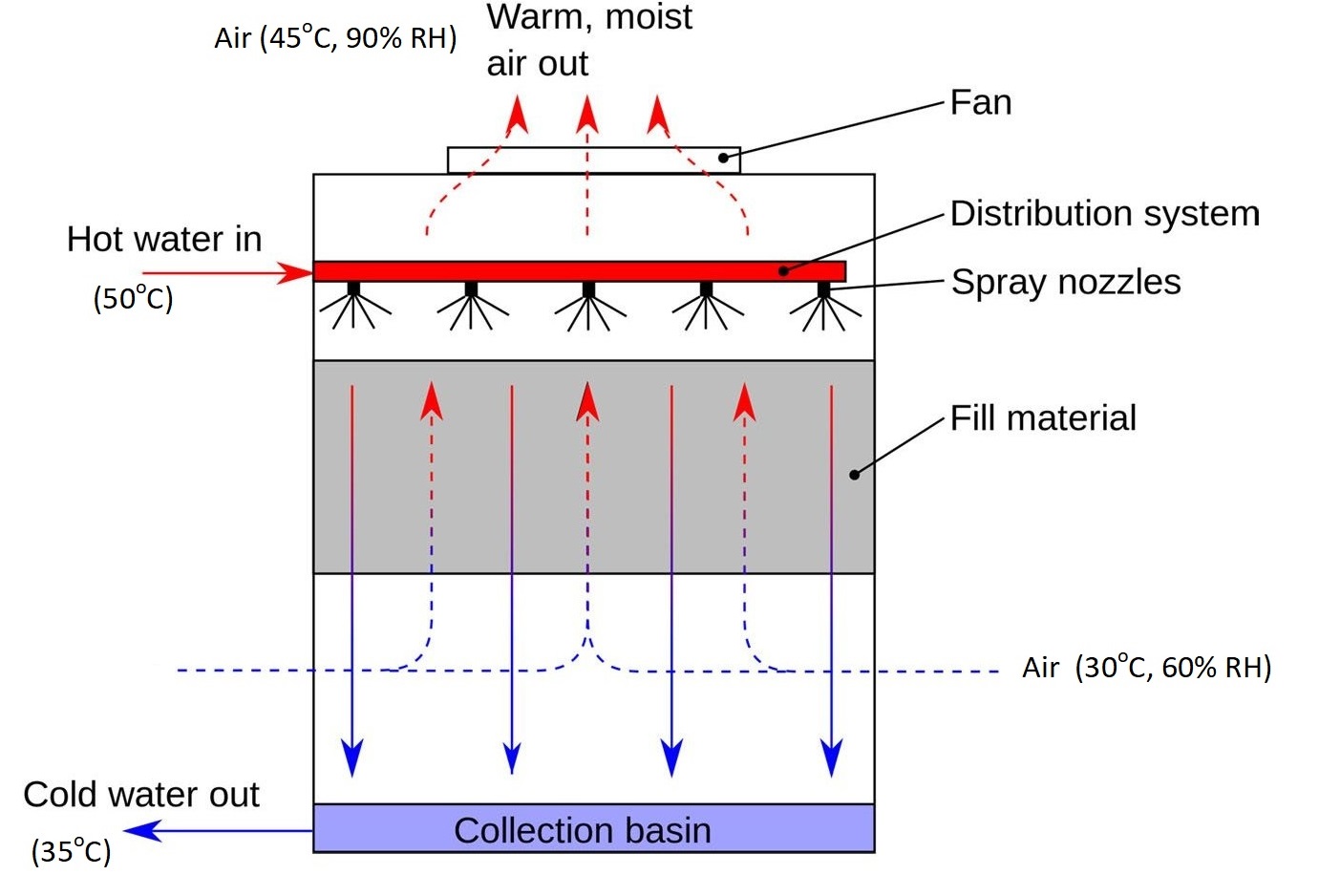
For the entry and exit conditions, kg of water vapor per kg of dry air, are obtained from the definition of absolute humidity (\(H_a\)), given as: \[H_a=\frac{\text{mass of water vapor}}{\text{mass of dry air}} = \frac{n_W}{n_A}\frac{M_W}{M_A} = \frac{P_W}{P-P_W} \frac{M_W}{M_A} \quad \frac{\text{kg vapor}} {\text{kg dry air}}\] where \(P_W\) is partial pressure of water vapor; and, \(P\) is total pressure. \(M_W, M_A\) are molecular weight of water and air respectively.
Vapor pressure of water (from table of data): \[\begin{aligned} \text{At }30^\circ\text{C} &: \ 31.8 \text{ mm Hg} \\ \text{At }45^\circ\text{C} &: \ 71.9 \text{ mm Hg} \end{aligned}\] From the definition of relative humidity (RH), we have \[\text{RH} = \frac{P_W}{P_W^{\text{sat}}}\] Hence, \[\begin{aligned} \text{inlet air} &: \text{30$^\circ$C, 60% RH} \qquad & P_W = 0.6\times31.8=19.08 \text{ mm Hg} \\ \text{exit air} &: \text{45$^\circ$C, 90% RH} & P_W = 0.9\times71.9= 64.71 \text{ mm Hg}\\\end{aligned}\]
The amount of water vapor in the inlet and exit are: \[\begin{aligned} \frac{19.08}{760-19.08}\times\frac{18}{29}= 0.016 \text{ kg water vapor/kg dry air} \\ \frac{64.71}{760-64.71}\times\frac{18}{29}= 0.058 \text{ kg water vapor/kg dry air} \end{aligned}\] Amount of water vapor picked-up per kg of air = \(0.058 - 0.016 = 0.042\) kg.
Amount of heat removal required for 15\(^\circ\)C drop in temperature for water = \(C_P\Delta\!T = 4.2\times15 = 63\) kJ/kg.
Average latent heat of water in the range of 30-45\(^\circ\)C = 2408 kJ/kg.
Water to be vaporized for removal of 63 kJ of energy removal = \(\dfrac{63}{2408} = 0.026\) kg.
0.042 kg of water vapor is picked-up by 1 kg of dry air (for the entry condition of 30\(^\circ\)C air with 60% RH, and exit condition of 45\(^\circ\)C air with 90% RH). Hence for 0.026 kg of water, we need: \[\frac{0.026}{0.042} = 0.62 \text{ kg of air}\]
For 1 kg of water, we need to contact it with 0.62 kg of air. So as to humidify the air, water is vaporizing to air. This leads to cooling of water.
Note: there is a loss of water to the air by the amount 0.026 kg per kg of water entering i.e., 2.6%.
