4. Fluid Mechanics
Pumps
Positive Displacement Pump
A positive displacement pump moves a fluid by repeatedly enclosing a fixed volume and moving it mechanically through the system. The pumping action is cyclic and can be driven by pistons, screws, gears, rollers, diaphragms or vanes. Two types of positive displacement pumps:
- reciprocating, and
- rotary
Reciprocating Pumps
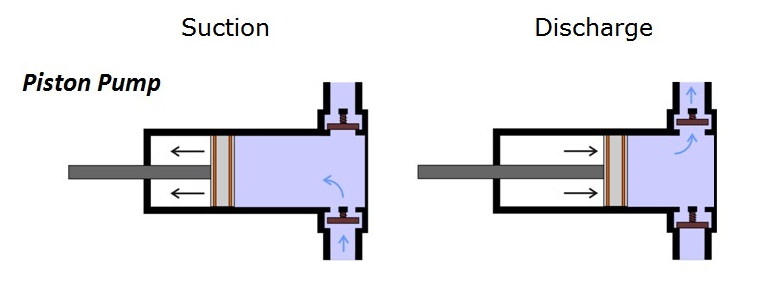
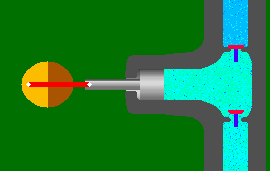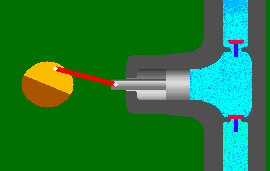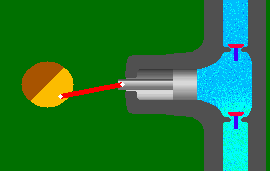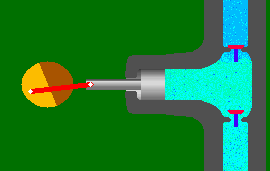
A reciprocating pump works by the repeated back-and-forth movement (strokes) of either a piston, plunger or diaphragm. These cycles are called reciprocation.
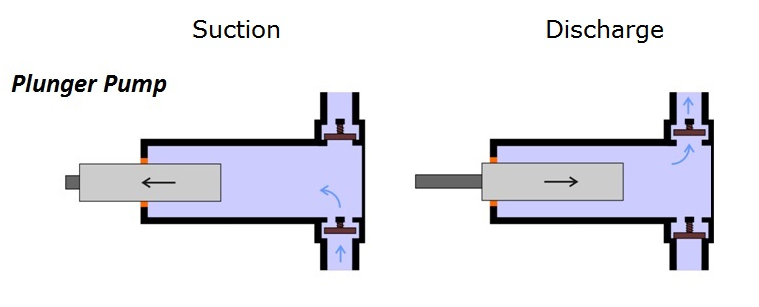
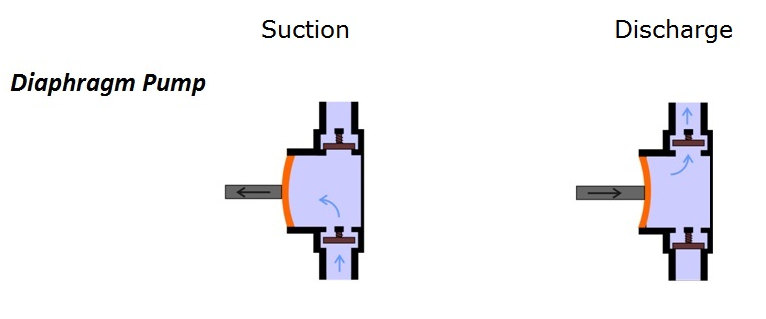
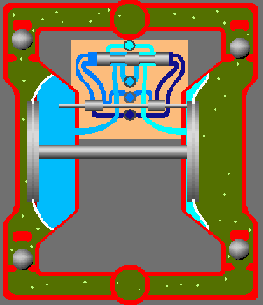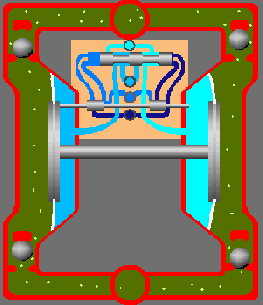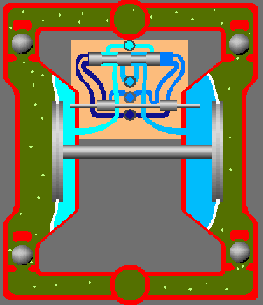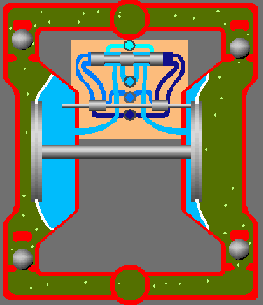
Rotary Pumps
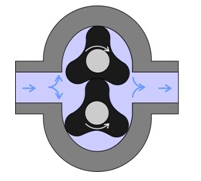
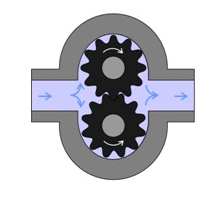
(a) External Gear Pump:An external gear pump consists of two interlocking gears supported by separate shafts. Rotation of the gears traps the fluid between the teeth moving it from the inlet, to the discharge, around the casing. No fluid is transferred back through the centre, between the gears, because they are interlocked.
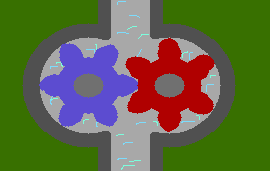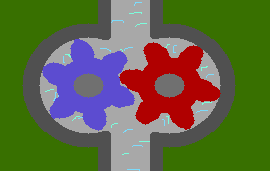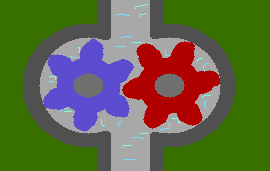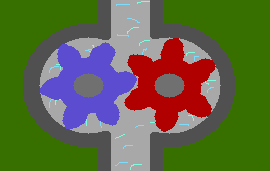
(b) Lobe Pump:
In the case of the lobe pump, the rotating elements are lobes instead of gears. The great advantage of this design is that the lobes do not come into contact with each other during the pumping action, reducing wear, contamination and fluid shear.