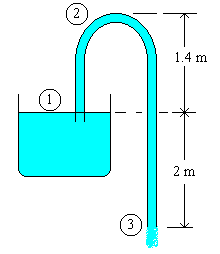
Siphon
Data:
Dia of tube = 3 cm = 0.03 m
Formula:
Bernoulli's equation for frictionless flow is \[ \displaystyle \frac{p}{\rho g} + \frac{v^2}{2g} + z = \text{ constant} \]
Discharge (Q) = cross sectional area x velocity
Calculations:
Applying Bernoulli's equation for the points 1 and 3, ( i.e. comparing the energy levels for the fluid in the tank surface and at the discharge point of tube)
p1 = 0 N/m2(g)
p3 = 0 N/m2(g)
z1 = 0 m
z3 = -2 m
Since the rate of fall of liquid level in the tank is almost negligible,
v1 = 0 m/sec.
Therefore,
0 + 0 + 0 = 0 + (v32 / 2g) - 2
v3 = (2 x 2g)0.5 = 6.265 m/sec
Q = (π/4)D2 v = (π/4) x 0.032 x 6.265 = 0.00443 m3/sec = 15.94 m3/hr
Applying Bernoulli's equation for the points 1 and 2, ( i.e. comparing the energy levels for the fluid at the tank surface to the peak point of siphon)
p1 = 0 N/m2(g)
z2 = 1.4 m
v2 = v3 = 6.265 m/sec (since the cross sectional area of sections 2 and 3 are the same)
0 + 0 + 0 = p2 / (ρg) + 6.2652 / (2g) + 1.4
p2 / (ρg) = -3.4 m
p2 = -3.4 x 1000 x 9.812 N/m2(g) = -33360.8 N/m2(g)
Absolute pressure at point 2 = 101325 - 33360.8 = 67964.2 N/m2(a)
