Rate Equation from CSTR data
From the following data find a satisfactory rate equation for the gas-phase decomposition of pure A, A -> R + S, in a mixed flow reactor.
τ based on inlet feed conditions, sec | 0.423 | 5.1 | 13.5 | 44.0 | 192 |
| XA (for CAo = 0.002 mol/lit) | 0.22 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.96 |
Calculations:
For the mixed flow reactor, the design equation is,
τ = CAoXA/-rA → 1
For variable density systems,
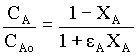
Where, εA = fractional change in volume = (VXA = 1 - VXA = 0) / VXA = 0 = (2 - 1)/1 = 1
Therefore,
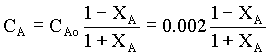 à 2
à 2
For the first order equation, equn.1 can be written as
τ = CAoXA/ kCA → 3
substituting for CAo in equation 3,
τ = 0.002 XA/ kCA
substituting for CA from equn.2,
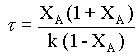
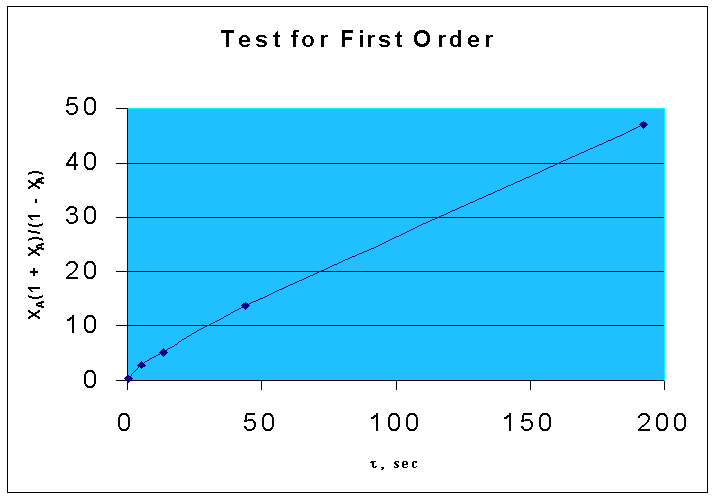
That is, if the given data is for a first order reaction, τ vs. XA(1 + XA)/(1 - XA) will be a straight line, with a slope of k.
τ, sec | 0.423 | 5.1 | 13.5 | 44 | 192 |
XA | 0.22 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.96 |
XA(1 + XA)/(1 - XA) | 0.3441 | 2.7754 | 5.25 | 13.7867 | 47.04 |
From the above data, the following graph is drawn :(graph 1)
For the second order equation, equn.1 can be written as
τ = CAoXA/ kCA2
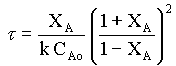
That is, if the given data is for a second order reaction, τ vs. XA(1 + XA)2/ (1 - XA)2 will be a straight line with a slope of kCAo.
τ, sec | 0.423 | 5.1 | 13.5 | 44 | 192 |
XA | 0.22 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.96 |
XA(1 + XA)2/(1 - XA)2 | 0.5382 | 12.2268 | 36.75 | 215.99 | 2304.96 |
From the above data, the following graph is drawn :(graph 2)
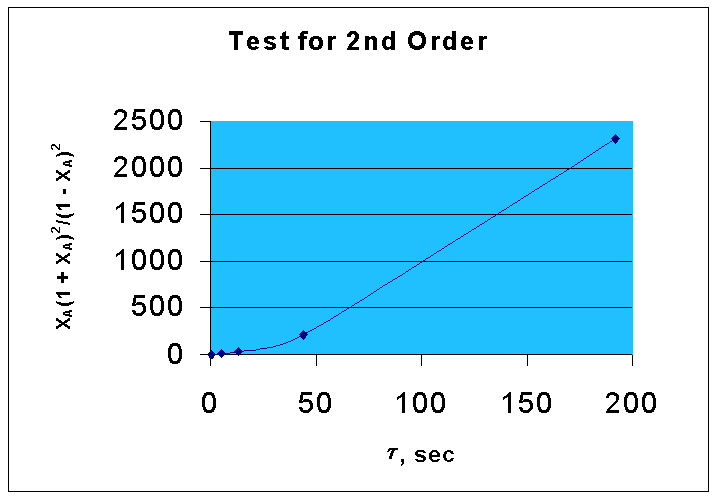
By comparing two graphs it is seen that first order kinetics is well fitting the given data.
That is, the reaction is following first order.
Slope = 0.2493 (from the graph.1)
Therefore,
k = 0.2493 sec-1.
Therefore, rate equation for the given reaction is
-rA = 0.2493 CAo (1 - XA)/(1 + XA) = 4.986 x 10-4 (1 - XA)/(1 + XA) mol/lit.sec
