Rate Equation from PFR data
The following conversion data were obtained in a tubular flow reactor for the gas-phase pyrolysis of acetone at 520oC and 1 atm.
CH3COCH3 -> CH3=C=O + CH4
Flow rate, g/hr 130 50 21 10.8 Conversion of acetone 0.05 0.13 0.24 0.35
The reactor was 80 cm long with 3.3 cm inner diameter. What rate equation is suggested?
Calculations:
Volume of reactor = (π/4)D2 L = 684 cm3 = 0.684 lit
Molecular weight of acetone = 12 + 3 + 12 + 16 + 12 + 3 = 58
The above flow rate data in g/hr are converted into gmol/hr, by dividing them with Molecular weight.
Flow rate, g/hr 130 50 21 10.8
Molal flow rate, gmol/hr (FAo) 2.2414 0.8621 0.3621 0.1862
Conversion of acetone (XA) 0.05 0.13 0.24 0.35
For the (tubular flow) plug flow reactor the design equation is,
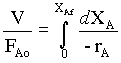
→ 1
CAo = pAo/RT = 1.01325 x 10-5/(8314 x (273 + 520))
= 0.01537 kmol/m3 = 0.01537 gmol/lit
For the first order reaction, (variable density systems)
-rA = kCA = kCAo(1 - XA)/(1 + εAXA) → 2
substituting for -rA from equn.2 in equn.1,
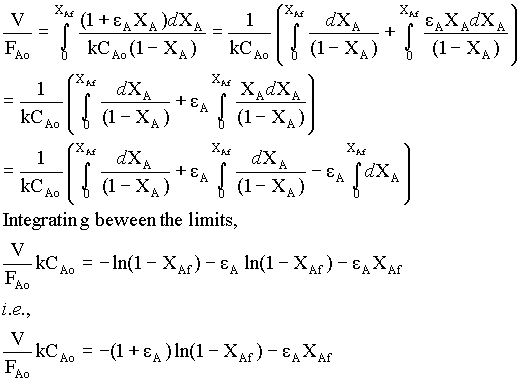
for the given gas-phase reaction, εA = (VXA = 1 - VXA = 0) / VXA = 0 = (2 - 1)/1 = 1
Therefore,
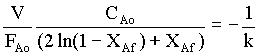
For the constant V and CAo,
FAo ( 2 ln(1 - XAf) + XAf) = -VCAok = constant. → 3
For second order reaction, (by Analytical integration)
k CAo2 V/FAo = 2εA(1 + εA) ln(1- XAf) + εA2XAf + (εA + 1)2 XAf/(1 + XAf)
For the given problem, εA = 1. Therefore,
(4 ln(1- XAf) + XAf + 4 XAf/(1 + XAf) ) FAo = k CAo2 V = constant. → 4
We will check the above relations for various data available.
Molal flow rate, gmol/hr (FAo) | 2.2414 | 0.8621 | 0.3621 | 0.1862 |
Conversion of acetone (XAf) | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.35 |
For First order: FAo ( 2 ln(1 - XAf) + XAf) | -0.11787 | -0.12804 | -0.11184 | -0.09525 |
For Second order: (4 ln(1- XAf) + XAf + 4 XAf/(1 + XAf) ) FAo | 0.124069 | 0.14712 | 0.146799 | 0.145369 |
From the tabulated data, it could be seen that the second order mechanism is well fitting the data, than first order.
Therefore, the reaction is following second order.
k CAo2 V = average of (4 ln(1- XAf) + XAf + 4 XAf/(1 + XAf) ) FAo for various FAo values
k CAo2 V = 0.146429 (obtained by omitting the first data)
Therefore, k = 0.146429 / (0.015372 x 0.684) = 906.2 lit/(gmol.hr)
And the equation is,
-rA = 906.2 CA2 gmol/(lit.hr)
Instead of analytical integration for 2nd order reaction, we can use numerical integration (Simpson's 1/3 rule)
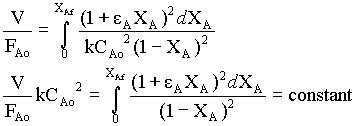
Numerical integration is obtained for the function
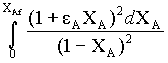
by taking 10 intervals.
Numerical Integration - by Simpson's rule | |||||||||||
0.05 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
0 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.015 | 0.02 | 0.025 | 0.03 | 0.035 | 0.04 | 0.045 | 0.05 | |
1 | 1.0202 | 1.0408 | 1.0618 | 1.0833 | 1.1052 | 1.1275 | 1.1503 | 1.1736 | 1.1974 | 1.2216 | |
0.0554 | |||||||||||
0.13 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
0 | 0.013 | 0.026 | 0.039 | 0.052 | 0.065 | 0.078 | 0.091 | 0.104 | 0.117 | 0.13 | |
1 | 1.0534 | 1.1096 | 1.1689 | 1.2314 | 1.2974 | 1.3670 | 1.4405 | 1.5182 | 1.6002 | 1.6870 | |
0.1707 | |||||||||||
0.24 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
0 | 0.024 | 0.048 | 0.072 | 0.096 | 0.12 | 0.144 | 0.168 | 0.192 | 0.216 | 0.24 | |
1 | 1.1008 | 1.2118 | 1.3344 | 1.4699 | 1.6198 | 1.7861 | 1.9708 | 2.1764 | 2.4057 | 2.6620 | |
0.4054 | |||||||||||
0.35 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
0 | 0.035 | 0.07 | 0.105 | 0.14 | 0.175 | 0.21 | 0.245 | 0.28 | 0.315 | 0.35 | |
1 | 1.1503 | 1.3237 | 1.5243 | 1.7572 | 2.0285 | 2.3459 | 2.7192 | 3.1605 | 3.6853 | 4.3136 | |
0.7807 | |||||||||||
XA | Area | FAo | FAo XA Area |
0.05 | 0.0554 | 2.2414 | 0.1241 |
0.13 | 0.1707 | 0.8621 | 0.1471 |
0.24 | 0.4054 | 0.3621 | 0.1468 |
0.35 | 0.7807 | 0.1862 | 0.1454 |
