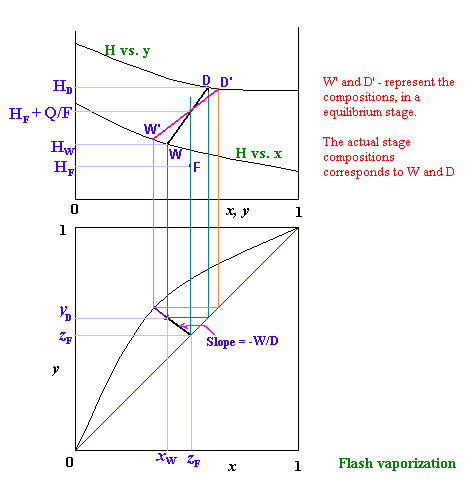
Flash Vaporization
A liquid mixture containing 50 mole % each of benzene and toluene at 40oC is to be continuously flash vaporized to vaporize 60 mole % of the feed. The residual liquid product contains 35 mole % benzene. If the enthalpies per mole of feed, the liquid product and the vapor product are respectively 2,5 and 30 kJ/mole,
- calculate the heat added in kJ per mole of vapor product
- represent the process on a H-x-y diagram
Data:
Basis: 100 mole of feed
Feed composition, mole fraction of more volatile component (zF) = 0.5
Feed (F) = 100 mole
Since 60% of the feed is vaporized,
Vapor (D) = 60 mole
Liquid (W) = 40 mole
Mole fraction of more volatile component in the liquid (xW) = 0.35
Formulae:
F = D + W → 1
FzF = DxD + WxW → 2
FHF + Q = DHD + WHW → 3
Calculations:
From equations, 1 and 2
100 x 0.5 = 60xD + 40 x 0.35
Therefore, xD = 0.6
From equation 3,
100 x 2 + Q = 60 x 30 + 40 x 5
Therefore, Q = 1800 kJ
Heat to be added per mole of vapor product = Q/D = 1800/60 = 300 kJ
The H-x-y diagram for the above process is given below: