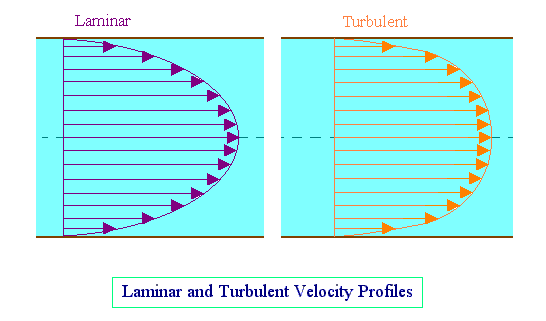
Velocity distribution in turbulent flow
No exact mathematical analysis of the conditions within a turbulent fluid has yet been developed, though a number of semi-theoretical expressions for the shear stress at the walls of a pipe of circular cross-section have been suggested.
The velocity at any point in the cross-section will be proportional to the one-seventh power of the distance from the walls. This may be expressed as follows:
\[\frac{u_x}{u_{CL}} = \begin{bmatrix}\frac{y}{r}\end{bmatrix}^{\frac{1}{7}}\]
Where ux is the velocity at a distance y from the walls, uCL the velocity at the centerline of pipe, and r the radius of the pipe.
This equation is referred to as the Prandtl one-seventh power law.
By using Prandtl one-seventh power law, the mean velocity of flow is found to be equal to 0.817 times the centerline velocity.